How Long Does It Take For Ovulation To Regulate?

Understanding How Long It Takes For Ovulation To Regulate Is Essential For Anyone Monitoring Their Menstrual Health Or Trying To Conceive. We Provide A Comprehensive, Research-Based Overview That Clarifies What Influences Ovulation, Why Regulation Can Vary, And What Signs Indicate That Your Cycle Is Returning To Its Natural Rhythm. While Individual Experiences Differ, Several Predictable Patterns Can Help You Better Understand Your Reproductive Timeline.
What Ovulation Regulation Really Means
Ovulation Regulation Refers To The Point At Which The Ovarian Cycle Settles Into A Consistent Pattern After A Period Of Irregularity. Predictable Cycles Typically Range From 21 To 35 Days, With Ovulation Occurring Approximately 12 To 16 Days Before The Next Expected Period. When Cycles Become Consistent, It Becomes Easier To Anticipate Fertile Windows And Understand Hormonal Patterns.
How Long Does It Typically Take For Ovulation To Regulate?
For Most Individuals, Ovulation Begins To Regulate Within Two To Six Months, Depending On The Underlying Cause Of Irregularity. However, Several Factors Can Shorten Or Extend This Timeline. Those Coming Off Hormonal Contraception, Experiencing Hormonal Shifts, Or Recovering From Stress-Related Cycle Disruptions May Require More Time For Hormones To Stabilise.
In Many Cases, The Body Needs Multiple Cycles To Re-Establish Normal Hormone Communication Between The Brain, Ovaries, And Endocrine System. A Few Irregular Months Are Common Before Regular Ovulation Patterns Are Restored.
Factors That Influence Ovulation Regulation
Hormonal Contraception Withdrawal
When Discontinuing Hormonal Birth Control, The Body Must Restart Its Natural Hormone Production Cycle. Ovulation May Regulate Within One To Three Months, Though Some People Experience Delays Of Up To Six Months. The Duration Depends On The Type Of Contraception Used, The Length Of Usage, And The Body’s Natural Hormonal Sensitivity.
Postpartum Hormonal Recovery
After Childbirth, Especially When Breastfeeding, Ovulation May Take Several Months To Over A Year To Fully Regulate. Prolactin Levels Suppress Ovulation, And Cycles Often Remain Irregular Until Breastfeeding Frequency Decreases.
Stress, Lifestyle, And Sleep Patterns

Chronic Stress, Sudden Weight Changes, And Sleep Disruption Can Interfere With Hormone Balance. Once Lifestyle Stabilises, Ovulation Often Regulates Within Two To Four Cycles.
Medical Conditions Affecting Ovulation
Conditions Such As Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Thyroid Disorders, And Pituitary Imbalances May Significantly Impact Ovulation Regularity. Regulation Time Varies But Often Requires Medical Guidance And Treatment To Establish Consistent Cycles.
Signs That Ovulation Is Becoming Regular
Consistent Cycle Length
One Of The Most Reliable Indicators Is A Steady Menstrual Cycle Pattern. When Your Cycle Varies By Only A Few Days Each Month, It’s A Strong Sign That Ovulation Is Occurring Predictably.
Regular Cervical Mucus Changes
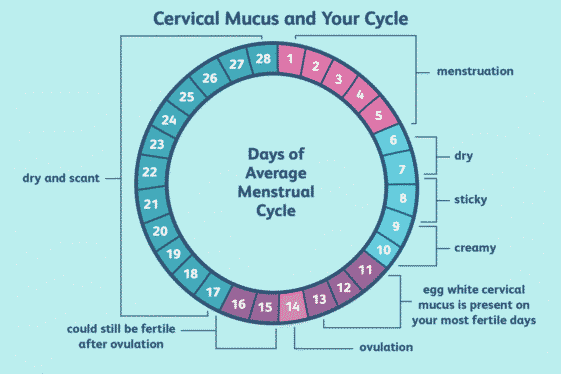
As Hormone Levels Stabilise, Cervical Mucus Will Show Clear Phases: Dry Days After Menstruation, Followed By Creamy Or Sticky Mucus, And Finally Stretchy, Egg-White Mucus During Ovulation.
Predictable Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Shifts
A Consistent Rise In BBT Following A Fertile Window Suggests That Progesterone Production Has Normalised, Indicating Regular Ovulation.
Cyclic Ovulation Symptoms
Mild Mid-Cycle Pelvic Sensations, Breast Tenderness, And Changes In Libido May Reappear Once Hormonal Patterns Become Stable.
How Long After Birth Control Does Ovulation Regulate?
Many Individuals Notice Regular Ovulation Resume Between Four To Twelve Weeks After Stopping Hormonal Birth Control. However, Some May Experience Temporary Anovulatory Cycles As The Body Adjusts.
Factors That Influence This Timeline Include:
- Type Of Contraception (Pill, Patch, Injection, Implant)
- Duration Of Use
- Underlying Hormonal Balance Prior To Contraceptive Use
- Metabolic And Lifestyle Factors
Those Coming Off Injectable Contraception May Experience The Longest Delays, Sometimes Taking Up To Ten Months Or More To Resume Predictable Cycles.
How Long Ovulation Regulation Takes After Pregnancy
Hormone Levels Fluctuate Significantly During And After Pregnancy. The Period Between Birth And The Return Of Regular Ovulation Varies Considerably.
Typical Timelines Include:
- Six To Twelve Weeks For Non-Breastfeeding Individuals
- Several Months To Over A Year For Those Exclusively Breastfeeding
- Gradual Regulation Of Cycles As Breastfeeding Frequency Reduces
It’s Normal For Several Cycles Postpartum To Be Irregular Before Predictable Ovulation Patterns Resume.
Lifestyle Practices That Support Ovulation Regulation
Balanced Nutrition
Consuming Adequate Protein, Healthy Fats, Whole Grains, And Micronutrient-Rich Foods Helps Stabilise Hormones And Support A Healthy Reproductive Cycle.
Consistent Sleep Patterns

Restful Sleep Regulates Cortisol, Melatonin, And Reproductive Hormones. Seven To Nine Hours Of Quality Sleep Can Positively Influence Ovulation Consistency.
Moderate Exercise
Regular Movement Supports Insulin Sensitivity And Hormonal Balance. However, Excessive Or Intense Exercise Can Delay Ovulation, Making Moderation Key.
Stress Management
Mindfulness Practices, Relaxation Techniques, And Work-Life Balance Significantly Help In Restoring Hormonal Equilibrium.
When To Seek Professional Evaluation

If Ovulation Does Not Regulate After Six Months, Or If Menstrual Cycles Are Extremely Irregular, It May Indicate An Underlying Hormonal Condition. Professional Evaluation Can Help Identify Issues Such As PCOS, Thyroid Dysfunction, Or Other Endocrine Imbalances.
You Should Also Seek Medical Guidance If You Experience:
- Extremely Painful Periods
- Very Heavy Or Very Light Bleeding
- Cycles Longer Than 45 Days Or Shorter Than 21
- No Period For Three Months Or More
- Difficulty Conceiving After One Year Of Trying (Or Six Months If Over Age 35)
Early Evaluation Often Leads To More Effective Treatment And Better Reproductive Outcomes.
Conclusion
Ovulation Regulation Is A Gradual Process Influenced By Hormonal Shifts, Lifestyle Factors, Medical Conditions, And Recent Contraceptive Or Postpartum Changes. While Many Individuals Experience Regular Ovulation Within Two To Six Months, Others May Require More Time For Hormones To Stabilise. Recognising The Signs Of Regulation And Supporting Your Body With Healthy Habits Can Promote A More Predictable Cycle.
For Those Tracking Fertility Or Trying To Conceive, Understanding These Patterns Offers Valuable Insight Into Reproductive Health And Timing.
